You have a tool like GIT or Maven that connects to a HTTPS website. Then your tool needs to know whether to trust that website’s certificate.
When that tool uses Java underneath, you can follow the following steps to add the website’s certificate to your keystore.
1) Visit the website [like for example https://maven.company.nl/nexus] using Firefox.
2) (optional) Confirm and add the exception if you get the notification “This Connection is Untrusted”
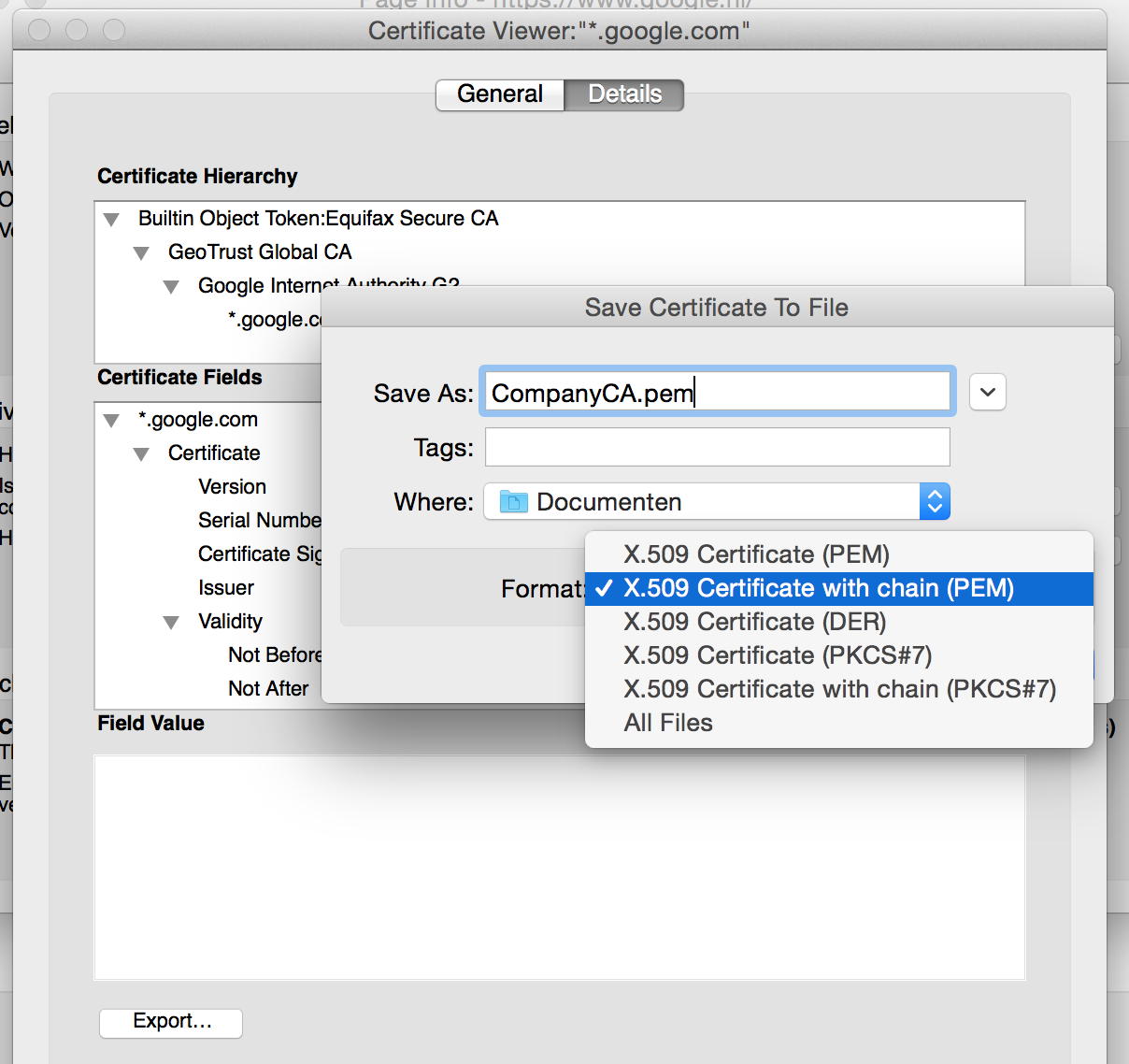
3) Export the certificate to a file with the name “CompanyCA.pem” ( click on lock left next to the domain name -> More information -> View certificate -> Details -> Export (choose format “X.509 Certificate with chain PEM”))
Export the certificate with format “X.509 Certificate with chain PEM”
4) Add the certificate to you cacerts keychain to the java version that maven uses via the following steps
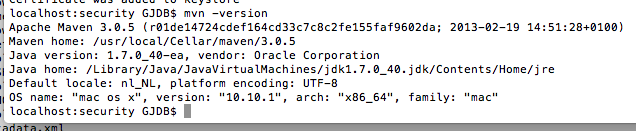
4.1) Determine which java version your maven uses via
mvn –version
4.2) On the command line, go to the java directory via
cd < java home directory >
Note: when you use Windows, then you need to start the command prompt as “Run as administrator”.
4.3) open the lib/security directory within this folder
4.4) Add the website’s CA certificate to the cacerts keychain via
keytool -keystore cacerts -importcert -alias companyca -file < file directory >/CompanyCA.pem
Note Replace the placeholder < file directory > with the file location where you stored the pem certificate. If you are on a unix like system, then you need to prefix this command with sudo.
Provide your password. By default this is changeit
![]()
When asked to trust it, type yes
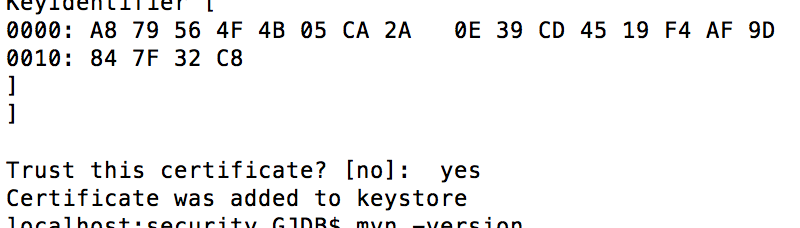
When the notification “Certificate was added to keystore” is shown without errors, then you are done!
Additionally
Do ensure that in your settings.xml and your pom files, all links to you repository point to the https url, so for example https://maven.company.nl/nexus
How do know your certificate is not trusted properly?
When you get one of the below exceptions…
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-deploy-plugin:2.7:deploy (default-deploy) on project parent: Failed to retrieve remote metadata nl.company:parent:1.5-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml: Could not transfer metadata nl.company:parent:1.5-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml from/to corporateRepo (https://maven.company.nl/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots): peer not authenticated -> [Help 1]
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-deploy-plugin:2.7:deploy (default-deploy) on project parent: Failed to retrieve remote metadata nl.company:parent:1.5-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml: Could not transfer metadata nl.company:parent:1.5-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml from/to corporateRepo (https://maven.company.nl/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots): sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target -> [Help 1]